Positioning, Navigation and Timing: Overview
Guidance on Positioning, Navigation and Timing (PNT), why it matters and the government framework for Greater PNT Resilience.
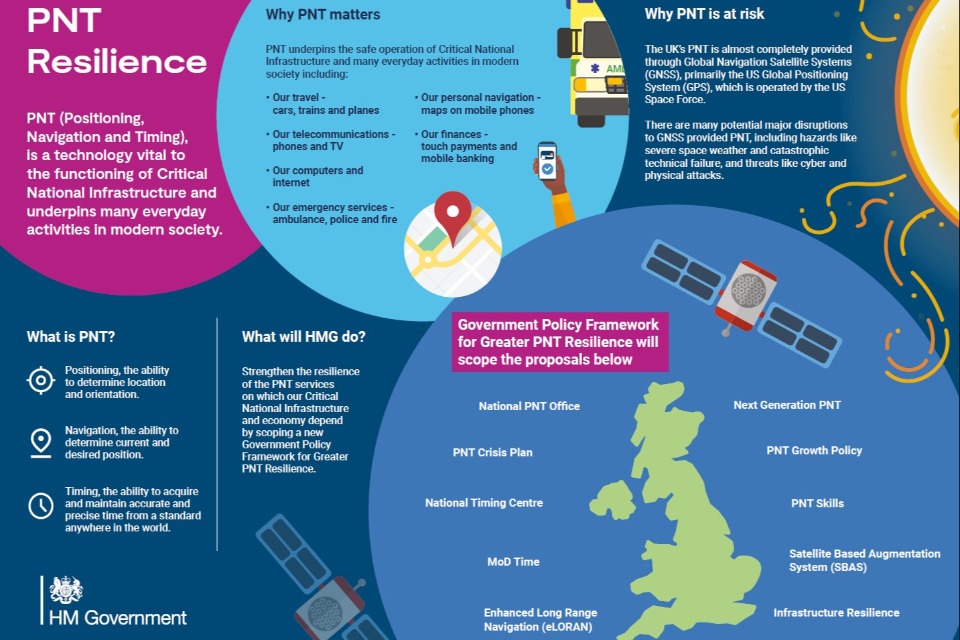
What is Positioning, Navigation and Timing (PNT)?
PNT stands for Positioning, Navigation and Timing:
-
Positioning: The ability to determine location and orientation.
-
Navigation: The ability to determine current and desired position.
-
Timing: The ability to acquire and maintain accurate and precise time from a standard anywhere in the world.
Why PNT matters and the risk of PNT loss
The UK鈥檚 PNT is almost completely provided through Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS), primarily the US Global Positioning System (GPS).
The 2018 Blackett Review on PNT (the GO-Science report 鈥楽atellite-derived Time and Position: A Study of Critical Dependencies鈥�) stated:
Global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) are often described as an 鈥渋nvisible utility鈥�. Signals transmitted from far above the Earth enable communications systems across the world. They enable the movement of goods and people, and facilitate the global supply lines that underpin our economy. They help to maintain electricity supply and support our emergency services.
However, our awareness of GNSS is out of step with our actual dependence upon it. In some sectors, the vulnerabilities of GNSS to both natural and ground-based interference, including through malicious attacks, are poorly understood. In others, there is insufficient protection against disruption, reducing our collective resilience to a loss of these systems.
PNT is vital to the functioning of Critical National Infrastructure (CNI) and underpins many everyday activities in modern society including transport, telecommunications, computers, emergency services, personal navigation and finances.
PNT matters to the UK economy. A 2023 report estimated the benefits of GNSS to be worth 拢13.62 billion per annum. The impact of a loss of GNSS for 7-days was estimated to be 拢7.64 billion, and 24 hours to be 拢1.42 billion.
There are many potential major disruptions to GNSS provided PNT, including hazards and threats like:
-
severe space weather
-
catastrophic technical failure
-
cyber attacks
-
physical attacks
Reports on PNT 谤颈蝉办蝉听听
There are a number of reports exploring the UK鈥檚 reliance on PNT provided by GNSS, its vulnerabilities and recommendations to address the risk of PNT 濒辞蝉蝉.听
These reports include:聽
-
The 鈥� this provides an overview of the UK鈥檚 reliance on PNT provided by GNSS and its vulnerabilities to potential disruptions.听听
-
The 2025 National Risk Register 鈥� this is the external version of the National Security Risk Assessment (NSRA) (the government鈥檚 assessment of the most serious risks facing the UK), and includes the risk of losing PNT services due to catastrophic technical failure of a GNSS constellation (network of satellites).
-
The 鈥� this provides recommendations to increase adoption of resilient PNT and address the risks from relying on vulnerable sources of PNT.
Framework for Greater PNT Resilience
In October 2023 the previous administration published the framework for Greater PNT Resilience to guide the government鈥檚 work on PNT (see above image). The framework remains in place under the current government. It sets out the current and future focus for PNT policy to improve PNT resilience across the Critical National Infrastructure (CNI) and wider economy, and drive growth. The framework that the government is working towards implementing includes commitments towards the following:
-
National PNT Office: establish a National PNT Office in the Department for Science, Innovation and Technology 鈥� to improve resilience and drive growth with responsibility for PNT policy, coordination, and delivery.
-
PNT Crisis Plan: retain and update a cross-government PNT Crisis Plan to be activated if GNSS provided PNT is lost and identify and implement short term mitigations.听听聽
-
National Timing Centre: develop a proposal for a National Timing Centre 鈥� to provide resilient, terrestrial, sovereign, and high-quality timing for the UK (UTC(NPL)), including sovereign components and optical clocks.听听
-
鈥楳OD Time鈥�: develop a proposal for 鈥楳inistry of Defence Time鈥� creating deeper resilience through a system of last resort and use National Timing Centre provided timing to support the Ministry of Defence.听听
-
eLORAN: develop a proposal for a resilient, terrestrial, and sovereign Enhanced Long-Range Navigation (eLORAN) system to provide backup Positioning and Navigation.听听聽
-
Infrastructure Resilience: rollout resilient GNSS receiver chips, develop holdover clocks, and consider options for legislation on CNI sectors to require minimum resilient PNT.听听
-
UK SBAS: develop a proposal for a UK Precise Point Positioning Satellite-Based Augmentation System (UK SBAS) to replace the UK鈥檚 use of the European Geostationary Navigation Overlay Service, monitor GNSS and enable GNSS dependent high accuracy Positioning for autonomous and precision uses.聽
-
PNT Skills: explore options for Centres for Doctoral Training in timing and PNT and review PNT skills, education, and training for long term sovereign PNT capability.听听
-
Growth Policy: develop a PNT growth policy, including R&D programmes, standards and testing, to drive innovation for PNT based productivity.听听
-
Next Generation PNT: deploy existing R&D funding into a UK Quantum Navigator and investigate possible options for a UK sovereign regional satellite system.听听
National Positioning, Navigation and Timing (PNT) Office
Following the publication of the framework, the National PNT Office was set up in the Department for Science, Innovation and Technology (DSIT). The office is responsible for PNT policy, coordination, and delivery and works across government to improve PNT resilience and drive growth.
Business best practice and principles for PNT resilience
On 20 November 2024 the Royal Institute of Navigation聽(RIN) launched the world鈥檚 first set of . The National PNT Office worked with the聽RIN聽on developing the principles and guidance including part funding the work.
The new guidance and checklist provide clear and actionable advice on how to assess and mitigate聽PNT聽risks, develop robust contingency plans, and invest in innovative聽PNT听迟别肠丑苍辞濒辞驳颈别蝉.